
中国稻米 ›› 2021, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 28-37.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2021.02.006
吴家青, 熊若愚, 解嘉鑫, 蒋海燕, 谭雪明, 潘晓华, 曾勇军, 石庆华, 曾研华*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-01-18
出版日期:2021-03-20
发布日期:2021-03-20
通讯作者:
曾研华
基金资助:
Jiaqing WU, Ruoyu XIONG, Jiaxin XIE, Haiyan Jiang, Xueming TAN, Xiaohua PAN, Yongjun ZENG, Qinghua SHI, Yanhua ZENG*( )
)
Received:2021-01-18
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2021-03-20
Contact:
Yanhua ZENG
摘要:
稻米食味品质是消费者评价稻米优劣的关键品质,决定了大米的档次与市场定位。本文阐述了直链淀粉含量、胶稠度、淀粉晶体结构、淀粉颗粒粒径分布、支链淀粉链长分布、淀粉溶解及膨胀特性、热力学特性、糊化特性及回生特性等稻米食味品质评价体系,从稻米淀粉合成相关酶(AGPase)、颗粒结合淀粉合成酶(GBSS)、可溶性淀粉合成酶(SSS)、淀粉分支酶(SBE)、淀粉脱分支酶(DBE)及蛋白组分概述了稻米食味品质的遗传调控。着重综述影响蛋白质含量的重要栽培因素——氮肥施用量、施用时期及氮肥形态对稻米食味品质形成的调控途径,对水稻食味品质的遗传研究及栽培调优进行了探讨与展望,可为水稻优良品种选育与生产、稻米在市场中的竞争力提升提供参考。
中图分类号:
吴家青, 熊若愚, 解嘉鑫, 蒋海燕, 谭雪明, 潘晓华, 曾勇军, 石庆华, 曾研华. 稻米食味品质形成及其响应氮素调控作用的研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2021, 27(2): 28-37.
Jiaqing WU, Ruoyu XIONG, Jiaxin XIE, Haiyan Jiang, Xueming TAN, Xiaohua PAN, Yongjun ZENG, Qinghua SHI, Yanhua ZENG. Research Advances on Rice Eating Grain Quality Formation and its Response to Nitrogen Application[J]. China Rice, 2021, 27(2): 28-37.
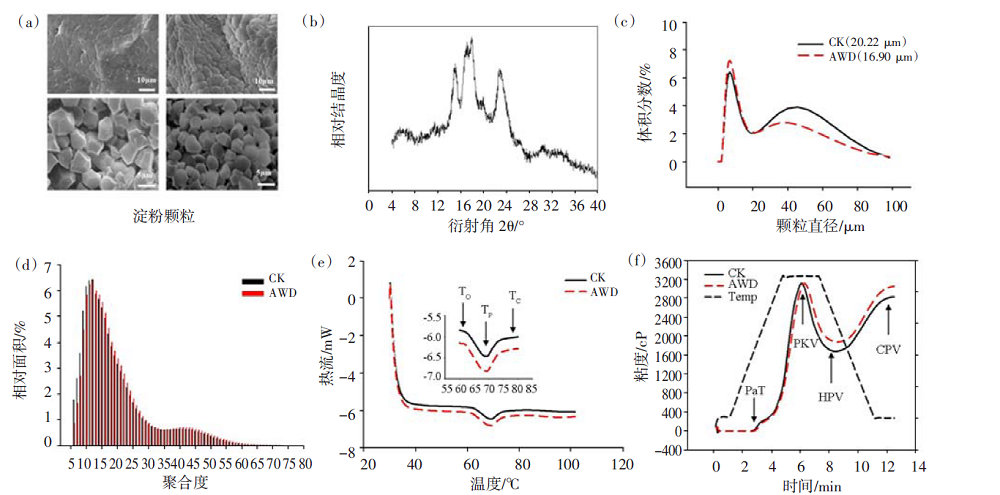
图1 稻米食味品质评价指标(a)扫描电镜下的淀粉颗粒(引自Ryoo等[35]);(b)水稻淀粉的X-射线衍射图;(c)水稻淀粉颗粒粒度分布曲线;(d)离子色谱系统分析支链淀粉链长分布;(e)水稻淀粉的热力学特性:To(起始温度),Tp(峰值温度),Tc(终止温度);(f)水稻淀粉的糊化特性:PaT(起始糊化温度),PKV(最高黏度),HPV(热浆黏度),CPV(冷浆黏度)。
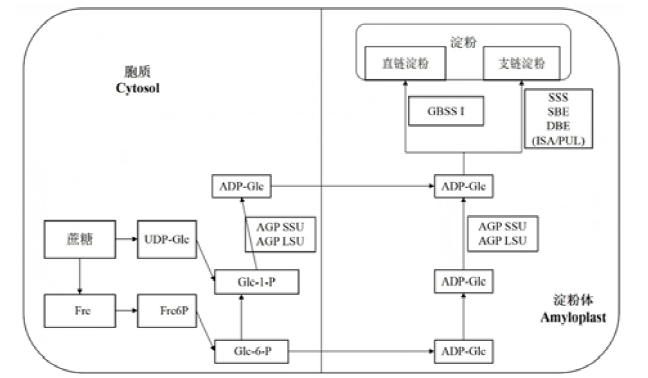
图2 水稻胚乳淀粉生物合成过程包含了蔗糖转化、ADPG的合成以及直链淀粉和支链淀粉的生成过程。UDP-Glc(UDP-葡萄糖);Frc(果糖);Frc-6-P(果糖-6-磷酸);Glc-1-P(葡萄糖-1-磷酸);Glc-1-P(葡萄糖-6-磷酸); ADP-Glc(ADP-葡萄糖);AGP SSU(腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶胞质型小亚基);AGP LSU(腺苷二磷酸葡萄糖焦磷酸化酶胞质型大亚基); GBSS I(颗粒结合淀粉合成酶Ⅰ)。
| [1] | BASHIR K, KHAN N M, RASHEED S, et al.Indica rice varietal development in Pakistan: an overview[J]. Paddy and Water Environment, 2007, 5(2): 73-81. |
| [2] | 李晏军. 中国杂交水稻技术发展研究(1964~2010)[D]. 南京:南京农业大学,2010. |
| [3] | VANDEPUTTE G E, DELCOUR J A.From sucrose to starch granule to starch physical behaviour: a focus on rice starch[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2004, 58(3): 245-266. |
| [4] | JULIANO B O.Structure, chemistry, and function of the rice grain and its fractions[J]. Cereal Food World, 2005, 57: 133-134. |
| [5] | ZHOU L, SHENG W, WU J, et al.Differential expressions among five Waxy alleles and their effects on the eating and cooking qualities in specialty rice cultivars[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2015, 14(6): 1 153-1 162. |
| [6] | HUANG L, LI Q, ZHANG C, et al.Creating novel Wx alleles with fine‐tuned amylose levels and improved grain quality in rice by promoter editing using CRISPR/Cas9 System[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, doi:10.1111/pbi.13391. |
| [7] | PEREZ S, BERTOFT E, SVWEIGES L.The molecular structures of starch components and their contribution to the architecture of starch granules: A comprehensive review[J]. Starch - Starke, 2010, 62(8): 389-420. |
| [8] | BLAZEK J.Role of amylose in structure-function relationship in starches from Australian wheat varieties [D]. Sydney :University of Sydney, 2009. |
| [9] | ZOBEL H F.Starch crystal transformations and their industrial importance[J]. Starch - Starke, 1988, 40(1): 1-7. |
| [10] | LIU J, ZHAO Q, ZHOU L, et al.Influence of environmental temperature during grain filling period on granule size distribution of rice starch and its relation to gelatinization properties[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2017, 76: 42-55. |
| [11] | BHAT F M, RIAR C S.Effect of amylose, particle size and morphology on the functionality of starches of traditional rice cultivars[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 92: 637-644. |
| [12] | BULEON A, COLONNA P, PLANCHOT V, et al.Starch granules: Structure and biosynthesis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 1998, 13(2): 93-112. |
| [13] | HIZUKURI S, TAKEDA Y, MARUTA N, et al.Molecular structures of rice starch[J]. Carbohydrate Research, 1989, 189: 227-235. |
| [14] | LU S.Correlations between the fine structure, physicochemical properties, and retrogradation of amylopectins from Taiwan rice varieties[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 1997, 74(1): 34-39. |
| [15] | HANASHIRO I, TAGAWA M, SHIBAHARA S, et al.Examination of molar-based distribution of A, B and C chains of amylopectin by fluorescent labeling with 2-aminopyridine[J]. Carbohydrate Research, 2002, 337(13): 1 211-1 215. |
| [16] | MUA J P, JACKSON D S.Fine structure of corn amylose and amylopectin fractions with various molecular weights[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 1997, 45(10): 3 840-3 847. |
| [17] | ACQUISTUCCI M C R. Isolation and physicochemical characterization of fonio (digitaria exilis stapf) starch[J]. Starch Starke, 1997, 49(4): 131-135. |
| [18] | CAI J, MAN J, HUANG J, et al.Relationship between structure and functional properties of normal rice starches with different amylose contents[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 125: 35-44. |
| [19] | SINGH J, MCCARTHY O J, SINGH H.Physico-chemical and morphological characteristics of New Zealand Taewa (Maori potato) starches[J].Carbohydrate Polymers, 2006, 64(4):569-581. |
| [20] | WANI A A, SINGH P, SHAH M A, et al.Rice starch diversity: Effects on structural, morphological, thermal, and physicochemical properties-A review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2012, 11(5): 417-436. |
| [21] | KAUR M, SINGH N.Studies on functional, thermal and pasting properties of flours from different chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars[J]. Food Chemistry, 2005, 91(3): 403-411. |
| [22] | NODA T, TAKAHATA Y, SATO T, et al.Physicochemical properties of starches from purple and orange fleshed sweet potato roots at two levels of fertilizer[J]. Starch/staerke, 1996, 48(11-12), 395-399. |
| [23] | COOKE D, GIDLEY M J.Loss of crystalline and molecular order during starch gelatinisation: origin of the enthalpic transition[J]. Carbohydrate Research, 1992, 227: 103-112. |
| [24] | LAURA ELIZABETH MORALES-MARTINEZ, LUIS ARTURO BELLO-PEREZ, MIMA MARIA SANCHEZ-RIVERA, et al. Morphometric, physicochemical, thermal, and rheological properties of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars indica × japonica[J]. Food & Nutrition Sciences, 2014, 5(3): 271-279. |
| [25] | BHAT F M, RIAR C S.Effect of composition, granular morphology and crystalline structure on the pasting, textural, thermal and sensory characteristics of traditional rice cultivars[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 280: 303-309. |
| [26] | DANG J M C, BASON M L. AACCI approved methods technical committee report: Collaborative study on a method for determining the gelatinization temperature of milled rice flour using the rapid visco analyser[J]. Cereal Foods World, 2014, 59(1): 31-34. |
| [27] | MAW Z, KENJI I.Quality assessment on Japonica and Indica rice genotypes based on rapid visco analyzer (RVA) pasting profile[J]. International Journal of Advanced Research, 2018, 6(1): 917-924. |
| [28] | YU S, MA Y, SUN D.Impact of amylose content on starch retrogradation and texture of cooked milled rice during storage[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2009, 50(2): 139-144. |
| [29] | YANG F, CHEN Y, TONG C, et al.Association mapping of starch physicochemical properties with starch synthesis-related gene markers in nonwaxy rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2014, 34(4): 1747-1763. |
| [30] | GUO J, HUANG Y, ZHANG J, et al.Preparation of oxidized starch using environment friendly chlorine dioxide as oxidant[J]. International Journal of Food Engineering, 2014, 10(2): 243-249. |
| [31] | LAWAL O S, LAPASIN R, BELLICH B, et al.Rheology and functional properties of starches isolated from five improved rice varieties from West Africa[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2011, 25(7): 1 785-1 792. |
| [32] | BAO J, SHEN S, SUN M, et al.Analysis of genotypic diversity in the starch physicochemical properties of nonwaxy rice: Apparent amylose content, pasting viscosity and gel texture[J]. Starch - Starke, 2006, 58(6): 259-267. |
| [33] | BAO J, WANG Y, SHEN Y.Determination of apparent amylose content, pasting properties and gel texture of rice starch by near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2007, 87(11): 2 040-2 048. |
| [34] | BAO J, KONG X, XIE J, et al.Analysis of genotypic and environmental effects on rice starch. 1. Apparent amylose content, pasting viscosity, and gel texture[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2004, 52(19): 6 010-6 016. |
| [35] | FUJITA N, YOSHIDA M, ASAKURA N, et al.Function and characterization of starch synthase i using mutants in rice[J]. Plant Physiology, 2006, 140(3): 1 070-1 084. |
| [36] | BAO J S.Rice Chemistry and Technology (Fourth Edition)[M]. Elsevier Inc, 2019: 55-108. |
| [37] | BO J.Rice grain quality: Problems and challenges[J]. Cereal Food World, 1990, 3(2): 245-253. |
| [38] | 赵艳岭. 中期氮肥调控影响水稻产量及稻米品质的生理机制[D]. 南京:南京农业大学,2014. |
| [39] | LEE S, HWANG S, HAN M, ECOM J, et al.Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2007, 65(4): 531-546. |
| [40] | OKAMURA M, HIROSE T, HASHIDA Y, et al.Starch reduction in rice stems due to a lack of OsAGPL1 or OsAPL3 decreases grain yield under low irradiance during ripening and modifies plant architecture[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2013, 40: 1 137-1 146. |
| [41] | ROSTI S, FAHY B, DENYER K.A mutant of rice lacking the leaf large subunit of adp-glucose pyrophosphorylase has drastically reduced leaf starch content but grows normally[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2007, 34(6): 480-489. |
| [42] | LEE S, EOM J, HWANG S, et al.Plastidic phosphoglucomutase and ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutants impair starch synthesis in rice pollen grains and cause male sterility[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2016, 67(18): 5 557-5 569. |
| [43] | WANG Z Y, WU Z L, XING Y, et al.Nucleotide sequence of rice waxy gene[J]. Nuclear Acids Research, 1990, 18: 5 898. |
| [44] | AYRES N M, MCCLUNG A M, LARLIN P D, et al.Microsatellites and a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germplasm[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1997, 94(6): 773-781. |
| [45] | ZHANG C, CHEN S, REN X, et al.Molecular structure and physicochemical properties of starches from rice with different amylose contents resulting from modification of OsGBSSI activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 2017, 65(10): 2 222-2 232. |
| [46] | HE P, LI S G, QIAN Q, et al.Genetic analysis of rice grain quality[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1999, 98(3-4): 502-508. |
| [47] | ALUKO G, MARTINEZ C, TOHME J, et al.QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa × O.glaberrima[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2004, 109(3): 630-639. |
| [48] | XU F F, SUN C, HUANG Y, et al.QTL mapping for rice grain quality: a strategy to detect more QTLs within sub-populations[J]. Molecular Breeding, 2015, 35: 105. |
| [49] | ZHANG C, ZHU J, CHEN S, et al.Wx, the ancestral allele of rice Waxy gene[J]. Molecular Plant, 2019, 12(8): 1 157-1 166. |
| [50] | OLSEN K M, PURUGGANAN M D.Molecular evidence on the origin and evolution of glutinous rice[J]. Genetics, 2002, 162(2): 941-950. |
| [51] | OLSEN K M.Selection under domestication: Evidence for a sweep in the rice Waxy genomic region[J]. Genetics, 2006, 173(2): 975-983. |
| [52] | 杨小雨. 基于淀粉精细结构解析粳米品质形成的理化基础[D]. 南京:南京农业大学,2015. |
| [53] | HIROSE T, TERAO T.A comprehensive expression analysis of the starch synthase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Planta, 2004, 220(1): 9-16. |
| [54] | GUAN H P.Starch biosynthesis: Understanding the functions and interactions of multiple isozymes of starch synthase and branching enzyme[J]. Trends Glycosci Glycotechnol, 1998, 10: 307-319. |
| [55] | GAO Z Y, ZENG D L, CUI X, et al.Map-based cloning of the ALK gene, which controls the gelatinization temperature of rice[J]. Science in China (Life Sciences), 2003, 46(6): 661-668. |
| [56] | UMEMOTO T, YANO M, SATOH H, et al.Mapping of a gene responsible for the difference in amylopectin structure between japonica-type and indica-type rice varieties[J]. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2002, 104(1): 1-8. |
| [57] | RYOO N, YU C, PARK C, et al.Knockout of a starch synthase gene OsSSIIIa/Flo5 causes white-core floury endosperm in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2007, 26(7): 1 083-1 095. |
| [58] | TOYOSAWA Y, KAWAGOE Y, MATSUSHIMA R, et al.Deficiency of starch synthase IIIa and IVb alters starch granule morphology from polyhedral to spherical in rice endosperm[J]. Plant Physiology, 2016, 170(3): 1 255-1 270. |
| [59] | HIROAKI Y, YASUNORI N.Organ specificity of isoforms of starch branching enzyme (q-enzyme) in rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 1992(7): 985-991. |
| [60] | MIZUNO K, KAWASAKI T, SHIMADA H, et al.Alteration of the structural properties of starch components by the lack of an isoform of starch branching enzyme in rice seeds[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1993, 268(25): 19 084. |
| [61] | NAKAMURA Y, UTSUMI Y, SAWADA T, et al.Characterization of the reactions of starch branching enzymes from rice endosperm[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2010, 51(5): 776-794. |
| [62] | MAN J, YANG Y, HUANG J, et al.Effect of simultaneous inhibition of starch branching enzymes I and IIb on the crystalline structure of rice starches with different amylose contents[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(41): 9 930-9 937. |
| [63] | SUN M, LEE H, ABDULA S, et al.Overexpression of starch branching enzyme 1 gene improves eating quality in japonica rice[J]. Journal of Plant Biotechnology, 2013, 40(2): 88-101. |
| [64] | TAKAYYKI S, FRANCIUSCO PB, SATOMI A, et al.Chlorella starch branching enzyme II (bell) can complement the function of bellb in rice endosperm[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2009, 50(6): 1 062-1 074. |
| [65] | SATOH H, NISHI A, YAMASHITA K, et al.Starch-branching enzyme I-deficient mutation specifically affects the structure and properties of starch in rice endosperm[J]. Plant Physiology, 2003, 133(3): 1 111-1 121. |
| [66] | NISHI A.Biochemical and genetic analysis of the effects of amylose-extender mutation in rice endosperm[J]. Plant Physiology, 2001, 127(2): 459-472. |
| [67] | FUJITA N, KUBO A, FRANCISCO P B, et al.Purification, characterization, and cDNA structure of isoamylase from developing endosperm of rice[J]. Planta, 1999, 208(2): 283-293. |
| [68] | NAKAMURA Y, UMEMOTO T, OGATA N, et al.Starch debranching enzyme (R-enzyme or pullulanase) from developing rice endosperm: purification, cDNA and chromosomal localization of the gene[J]. Planta, 1996, 199(2): 209-218. |
| [69] | UTSUMI Y, NAKAMURA Y.Structural and enzymatic characterization of the isoamylase1 homo-oligomer and the isoamylase1-isoamylase2 hetero-oligomer from rice endosperm[J]. Planta, 2006, 225(1): 75-87. |
| [70] | UTSUMI Y, UTSUMI C, SAWADA T, et al.Functional diversity of isoamylase oligomers: The isao homo-oligomer is essential for amylopectin biosynthesis in rice endosperm[J]. Plant Physiology, 2011, 156(1): 61-77. |
| [71] | YUN M, UMEMOTO T, KAWAGOE Y.Rice debranching enzyme isoamylase3 facilitates starch metabolism and affects plastid morphogenesis[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2011, 52(6): 1 068-1 082. |
| [72] | LI Q, ZHANG G, DONG Z, et al.Characterization of expression of the OsPUL gene encoding a pullulanase-type debranching enzyme during seed development and germination in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 47(5): 351-358. |
| [73] | TAKASHIMA Y, SENOURA T, YOSHIZAKI T, et al.Differential chain-length specificities of two isoamylase-type starch-debranching enzymes from developing seeds of kidney bean[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2007, 71(9): 2 308-2 312. |
| [74] | FUJITA N, TOYOSAWA Y, UTSUMI Y, et al.Characterization of pullulanase (PUL)-deficient mutants of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and the function of PUL on starch biosynthesis in the developing rice endosperm[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2009, 60(3): 1 009-1 023. |
| [75] | NING H F,QIAO J F,LIU Z H, et al.Distribution of proteins and amino acids in milled and brown rice as affected by nitrogen fertilization and genotype[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2010, 52: 90-95. |
| [76] | 杨静,罗秋香,钱春荣,等. 氮素对稻米蛋白质组分含量及蒸煮食味品质的影响. 东北农业大学学报,37(2):145-150. |
| [77] | 石吕,张新月,孙惠艳,等. 不同类型水稻品种稻米蛋白质含量与蒸煮食味品质的关系及后期氮肥的效应[J]. 中国水稻科学,2019,33(6):541-552. |
| [78] | 高辉,马群,李国业,等. 氮肥水平对不同生育类型粳稻稻米蒸煮食味品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2010,43(21):4 543-4 552. |
| [79] | 柳金来,宋继娟,周柏明,等. 氮肥施用量与水稻品质的关系[J]. 土壤肥料,2005(1):17-19. |
| [80] | 从夕汉,施伏芝,阮新民,等. 氮肥水平对不同基因型水稻氮素利用率、产量和品质的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2017,28(4):1 219-1 226. |
| [81] | 曾光春. 攀西地区氮肥运筹对水稻产量及品质的影响[D]. 成都:四川农业大学,2003. |
| [82] | 马群. 氮肥施用量对不同类型品种稻米品质的影响[D]. 扬州:扬州大学,2008. |
| [83] | 陈莹莹,胡星星,陈京都,等. 氮肥水平对江苏早熟晚粳稻食味品质的影响及其品种间差异[J]. 作物学报,2012,38(11):2 086-2 092. |
| [84] | BRYANT R,YEATER K, MCCLUNG A M.Effect of nitrogen rate and the environment on physicochemical properties of selected high-amylose rice cultivars[J]. Cereal Chemistry, 2015, 92(6): 604-610. |
| [85] | 宁慧峰. 氮素对稻米品质的影响及其理化基础研究[D]. 南京:南京农业大学,2011. |
| [86] | ZHU D, ZHANG H, GUO B, et al.Effects of nitrogen level on structure and physicochemical properties of rice starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2017, 63: 525-532. |
| [87] | 黎星,汪勇,成臣,等. 氮肥运筹对南方优质常规晚粳产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国稻米,2019,25(1):29-33. |
| [88] | 蒋鹏,熊洪,张林. 施氮量和氮肥运筹模式对糯稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 作物研究,2015,29(6):595-598. |
| [89] | 赵可,许俊伟,姜元华,等. 施氮量和品种类型对稻米食味品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(21):63-67. |
| [90] | GU J, CHEN J, CHEN L, et al.Grain quality changes and responses to nitrogen fertilizer of japonica rice cultivars released in the Yangtze River Basin from the 1950s to 2000s[J]. The Crop Journal, 2015,3(4): 285-297. |
| [91] | SINGH N, PAL N, MAHAJAN G, et al.Rice grain and starch properties: Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2011, 86(1): 219-225. |
| [92] | YANG X, BI J, GILBERT R G, et al.Amylopectin chain length distribution in grains of japonica rice as affected by nitrogen fertilizer and genotype[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2016, 71: 230-238. |
| [93] | CAO X M, SUN H Y, WANG C G, et al.Effects of late-stage nitrogen fertilizer application on the starch structure and cooking quality of rice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture, 2017, 98(6): 2 332-2 340. |
| [94] | 胡群,夏敏,张洪程,等. 氮肥运筹对钵苗机插优质食味水稻产量及品质的影响[J]. 作物学报,2017,43(3):420-431. |
| [95] | ZHU D, ZHANG H, GUO B, et al.Effect of nitrogen management on the structure and physicochemical properties of rice starch[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(42): 8 019-8 025. |
| [96] | 杨泽敏,王维金,蔡明历,等. 氮肥施用期及施用量对稻米品质的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报,2002 (5):429-434. |
| [97] | JIANG Q, DU Y, TIAN X, et al.Effect of panicle nitrogen on grain filling characteristics of high-yielding rice cultivars[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2016, 74: 185-192. |
| [98] | XIONG F, WANG Z, GU Y, et al.Effects of nitrogen application time on caryopsis development and grain quality of rice variety yangdao 6[J]. Rice Science, 2008, 15(1): 57-62. |
| [99] | TANG S, ZHANG H, LIU W, et al.Nitrogen fertilizer at heading stage effectively compensates for the deterioration of rice quality by affecting the starch-related properties under elevated temperatures[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 277: 455-462. |
| [100] | 罗刚. S型控释氮肥对水稻产量形成、养分吸收利用的影响[D]. 扬州:扬州大学,2016. |
| [101] | 金正勋,秋太权,孙艳丽,等. 氮肥对稻米垩白及蒸煮食味品质特性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2001,7(1):31-35. |
| [102] | 彭玉,马均,蒋明金,等. 缓/控释肥对杂交水稻根系形态、生理特性和产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2013,19(5): 1 048-1 057. |
| [103] | 王玉军,邹应斌,张夫道. 掺混型缓/控释肥对杂交晚稻产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料,2009(5):28-33. |
| [104] | 李武,邓飞,胡慧,等. 缓控释氮肥对机插杂交籼稻稻米品质的影响[J]. 核农学报,2018,32(4): 779-787. |
| [105] | ZHU D, ZHANG H, GUO B, et al.Effects of nitrogen level on yield and quality of japonica soft super rice[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2017, 16(5): 1 018-1 027. |
| [1] | 王岩, 王旺, 蔡嘉鑫, 曾鑫, 倪新华, 田洁, 唐闯, 景秀, 周苗, 王晶, 徐昊, 胡雅杰, 邢志鹏, 郭保卫, 许轲, 张洪程. 氮肥对稻米淀粉结构及理化性质影响的研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 1-8. |
| [2] | 胡江博, 任正鹏, 丁翔, 王朝全, 冯阳, 王笑见, 张翔, 胥南飞. 稻田除草剂应用现状与抗除草剂水稻育种研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 13-19. |
| [3] | 王云翔, 咸云宇, 赵灿, 王维领, 霍中洋. 缓控释氮肥施用技术在水稻上应用研究进展与展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 20-26. |
| [4] | 李逸翔, 周新桥, 陈达刚, 郭洁, 陈可, 张容郡, 饶刚顺, 刘传光, 陈友订. 高γ-氨基丁酸水稻及其米制食品开发应用研究进展[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 38-44. |
| [5] | 薛莲, 段圣省, 郑兴飞, 殷得所, 董华林, 胡建林, 王红波, 查中萍, 郭英, 曹鹏, 徐得泽. 湖北省水稻生产发展现状及对策建议[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 45-47. |
| [6] | 王昕, 刘炜, 马洪文, 贺奇, 冯伟东, 张益民, 李虹, 殷延勃. 宁夏优质稻育种历程、问题及展望[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 48-52. |
| [7] | 孙志广, 刘艳, 李景芳, 周振玲, 邢运高, 徐波, 周群, 王德荣, 卢百关, 方兆伟, 王宝祥, 徐大勇. 水稻萌发耐淹性鉴定评价方法研究及种质资源筛选[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 53-58. |
| [8] | 王兴为, 王志成. 秸秆还田与深施氮肥对水稻叶片生理特征、氮素利用及产量的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 59-65. |
| [9] | 赫兵, 李超, 严永峰, 刘月月, 赫靖淇, 于天华, 王帅, 陈殿元, 严光彬. 水稻秸秆秋季水耙浆还田对土壤及水稻性状的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 66-71. |
| [10] | 董维, 张建平, 邓伟, 徐雨然, 奎丽梅, 涂建, 张建华, 安华, 王睿, 谷安宇, 张锦文, 吕莹, 杨丽萍, 管俊娇, 陈忆昆, 李小林. 云南省1983—2021年审定水稻品种基本特性分析[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 84-89. |
| [11] | 吴涛, 邓宏中, 赵迎曦, 杨琛, 郭昱, 赵有权, 谢志梅, 张立阳, 杨远柱. 隆平高科水稻绿色通道2016—2021年审定品种分析[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 90-94. |
| [12] | 邵泽毅, 谭旭生, 伍斌, 管恩相. 稻田小龙虾轮捕轮放寄养技术浅析[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 98-100. |
| [13] | 黄日伟, 廖春良, 梁月宽, 杨绍意, 尚子帅, 姚云峰. 华浙优261在广西不同海拔作早中晚稻种植表现及高产栽培技术[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 106-107. |
| [14] | 郑红明, 郑品卉. 浅析稻谷比价偏低对我国水稻产业的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(4): 32-37. |
| [15] | 严如玉, 甘国渝, 赵希梅, 殷大聪, 李燕丽, 金慧芳, 朱海, 李继福. 我国水稻优势产区生产格局及施肥现状研究[J]. 中国稻米, 2023, 29(3): 1-8. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||